What's the Difference Between Rolled and Cut Thread Bolts - Classic Metallic
Rolled and Cut Thread Bolts
Threads of a mechanical fastener, whether or not it is a headed bolt, rod, or twisted bolt, can be produced by one or the other by cutting or rolling. the threads were made on a specific size bolt or screw that we stock. The primary explanation we are posed this inquiry is because "rolled" threads are seen to be better than "cut" threads on remotely threaded fasteners.
Rolled Thread Bolts
When a thread is made by rolling, it utilizes a course of cold forming, where the clear piece is passed between either hardened steel plates or round kicks the bucket. These kicks in the bucket will have either the thread pitch or a standard section machined into their face, contingent upon the specific thread rolling sort and cycle being utilized, and as the clear disregard them.
The course of roll threading a bolt is a virus-shaping cycle utilizing a bunch of hardened steel that bites the dust to frame threads onto a bolt. The bite of the dust juts into the external distance across the clear bolt to shape threads onto the bolt. As the bolt is feeling the squeeze, the steel grain streams in various headings, making the bolt more grounded, as it doesn't change the structural integrity of the steel. Rolled thread bolts are likewise smoother in the establishment and more impervious to damage because them being hardened and compressed.
Advantages
More efficient cycle as they are less work concentrated.
By deforming and cold working the bolt in the rolling system the bolt becomes more grounded (without tears and cracks of a cut thread) - thus stronger.
Rolled threads are smoother.
Cut Thread Bolts
Cut threading bolts includes severing the steel's grain structure to produce threads. While rolled thread bolts offer some advantages over cut thread bolts concerning strength and cost, cut threads can be made to virtually all specifications, including larger-diameter bolts. Birmingham Fastener has the capacity for thread cutting up to 4 inches in diameter.
Advantages
Can meet practically all specifications.
Bolts can be fabricated to more unambiguous size and layered prerequisites with few restrictions concerning their diameter and the thread length.
Can make bolts at a lot higher diameters than the rolled thread process.
A straightforward arrangement is great for little group runs.
Difference between Rolled and Cut Thread Bolts
Machined threading (cut threads) comprises eliminating material. The metal is cut away in a few progressive strides with a significant loss of material. The strands of the material are in this manner "cut" and broken.
The mechanical strength of a threaded component is hence impacted by the threading system. The qualities of a rolled thread compared to a cut thread can be summed up as follows:
Tensile strength -> up to 10% higher
Shear strength -> better, due to the crack propagation mode
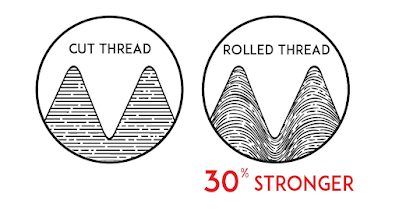
Fatigue strength -> up to 30% higher
The functioning burden cut-off points and safety coefficients of a lifting ring fabricated with a rolled thread can in this manner be a lot higher than those of the equivalent lifting ring with a cut thread. Fabricating mechanical parts utilizing the thread rolling cycle comprises deforming a section under the power of pivoting presses. The material is accordingly distorted by cold forming and not cut. This distinction of thread rolling outcomes in superior tensile strength.
1. Static Tensile Strength: As the metal fiber isn't cut, the thread rolling interaction normally expands the thread strength. The cross-sectional view underneath exhibits the contrast between the two strategies: rolled thread (twisted material) and cut thread (cut material).
2. Material Hardness and Fatigue Strength: One of the qualities of thread rolling is the solidifying of the part. At the lower part of the thread, a zone of extremely high pressure, the material can be distorted up to 200 percent. This extraordinarily builds the surface hardness of the material and creates a condition of pressure that forestalls the development of cracks and their propagation, which likewise brings about better fatigue resistance. Solidly, the fatigue strength of cold-rolled threads can ultimately depend on 30% higher compared to cut threads.
Outlook
Opting for rolled thread bolts implies more limited work times and considerably lower costs. The lower cost of roll threaded bolts likewise comes from the more modest body diameter; a more modest body implies less weight and significantly, fewer materials and assets utilized for heat-treating, stirring, plating, et cetera. Also, the burnishing impact of the rolling makes the bolts smoother, while the cold working makes them overall more resilient to damage.
If you want quality Industrial fasteners for your business, you can call us at +971-506349042, +971 6 575 1335. Or Visit Our Website https://classicmetallic.com/
Email us at sales@clmet.com/info@clmet.com for ordering industrial fasteners.







Comments
Post a Comment