Heat Treatment for Bolts and Fasteners | Heat Tempered Bolts
 |
| Heat Treatment for Bolts and Fasteners |
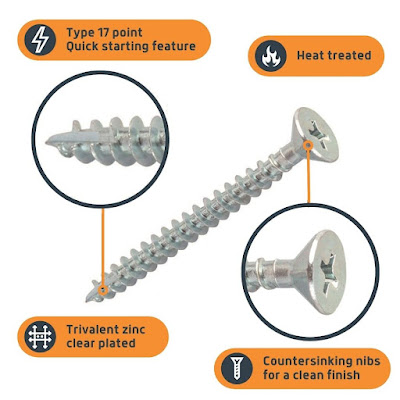
A portion of the physical properties of bolts and fasteners can be modified through warm treatment after introductory development. Specifically, steel combinations are heat treated regularly to build their solidarity, hardness, and other such properties.
Oil and gas, petrochemical, synthetic, and power age plants contain boilers, pressure piping vessels, valves, and interaction gear requiring high-strength dashing to keep up with seal closure on flanged joints, fittings, and terminations. Heat-treated bolts are essential to bear the tensile stresses within the bolts. High horsepower industrial mixers and pump drive shafts usually involve the higher shear strength provided by heat-treated bolts or pins.
Importance of Heat Treatment of Bolts & Fasteners
There are different standards governing the heat treatment of bolts and fasteners. The two most normal principles are from the SAE International (Society of Automotive Engineers) and ASTM global (American Society for Testing and Materials). There are additional norms from every association covering consumption opposition, high and low-temperature openness, and other physical boundaries that require particular fasteners.
High-strength or heat-treated bolts and fasteners are frequently expected to deal with the tensile, shear, or combination loads on the darted joints in requesting applications. Various demanding applications require high-strength fasteners to deal with high tensile and shear stresses created by the applied burdens on the bolted or fastened joints.
The heat treatment process utilizes cooling and heating activities applied on composites or metals in the strong condition of the issue. Bolts and fasteners are exposed to heat to accomplish modification in rigidity, smoothness, malleability, and material strength. The microstructure of the metal parts is adjusted by the most common way of strengthening to dial down the assembling activity.
What is the Process of Heat Treatment of Bolts & Fasteners?
Steel alloys with higher carbon and alloying components can be through solidified and changes will happen all through the part even at lower cooling rates, which diminishes remaining pressure and mutilation during heat treatment. In lower hardenability alloys, solidifying will just happen part way into the composite from the surface. The chemistry of an element plays an important role in influencing the reaction of heat treatment and the capacity of the fastener to carry out its planned operation.Case Hardening – this process involves hardening the outer layer of the metal/socket screw/fastener whilst retaining a soft inner metal core.
Annealing – adjusts the physical and chemical design of the metal/socket screw/fastener which permits it to be extended under tensile pressure. It is utilized to lessen hardness, increment ductility, and assist in eliminating internal stresses.
Normalizing – this gives the metal/socket screw/fastener a uniformed and fine grain structure
Tempering – this process heats the metal/socket screw/fastener to a precise temperature below the critical point and is usually carried out in the air, vacuum, or inert atmosphere.
Outlook
Using heat-treated bolts and fasteners in a design can give structural advantages. In many cases, heat-treated bolts will have higher costs in comparison with unhardened, low-carbon steel bolts. Equipment failure can possibly result if heat-treated or high-strength bolts are replaced with softer bolts during a redesign, retrofit, or update activity.
If you want quality Industrial fasteners for your business, you can call us at +971-506349042, +971 6 575 1335. Or Visit Here: www.classicmetallic.com
Email us at sales@clmet.com / info@clmet.com for ordering industrial fasteners.





Comments
Post a Comment